Transform Your CAE Simulation and Design Workflow
Transform your CAE simulation and design flow by integrating advanced tools and features automating tasks to reach appropriate results. Accurate simulations allow you to significantly reduce the number of prototypes needed in your development process
The core function of CAE solutions is to minimize prototype iterations by providing reliable simulations. This includes conducting stress analysis and both static and dynamic evaluations across various sectors, such as automotive, aerospace, medical devices, and other industrial applications.
At Varphi, our expertise encompasses a wide range of CAE solutions, including structural analysis, aerodynamics, thermal analysis, and safety assessments, ensuring comprehensive support for your design needs.
Advanced Engineering Solutions provided by our CAE, CFD & FEA experts
We deliver Advanced Engineering Services for Product Development, Systems Engineering and Manufacturing Engineering.
LEADING INDUSTRIAL SOLUTIONS PROVIDER INDIA
With exceptional service and expertise in technology and innovation
Improvise your products and optimize workflows with our advanced Computer-Aided Engineering (CAE) and Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) solutions.
CAE Solutions
CAE Solutions
Our CAE solutions leverage advanced simulation and analysis tools to optimize product designs, improve performance, and reduce development time. These solutions empower engineers to make data-driven decisions and enhance overall efficiency.
CFD Solutions
CFD Solutions
Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) uses numerical methods to analyze fluid flow, heat transfer, and related phenomena. It enables engineers to visualize and optimize designs for enhanced performance and efficiency.
FEA Solutions
FEA Solutions
Our FEA (Finite Element Analysis) solutions offer powerful simulation tools to assess structural integrity, predict behavior under various conditions, and optimize designs. This approach helps engineers ensure safety, enhance performance, and reduce costs effectively.
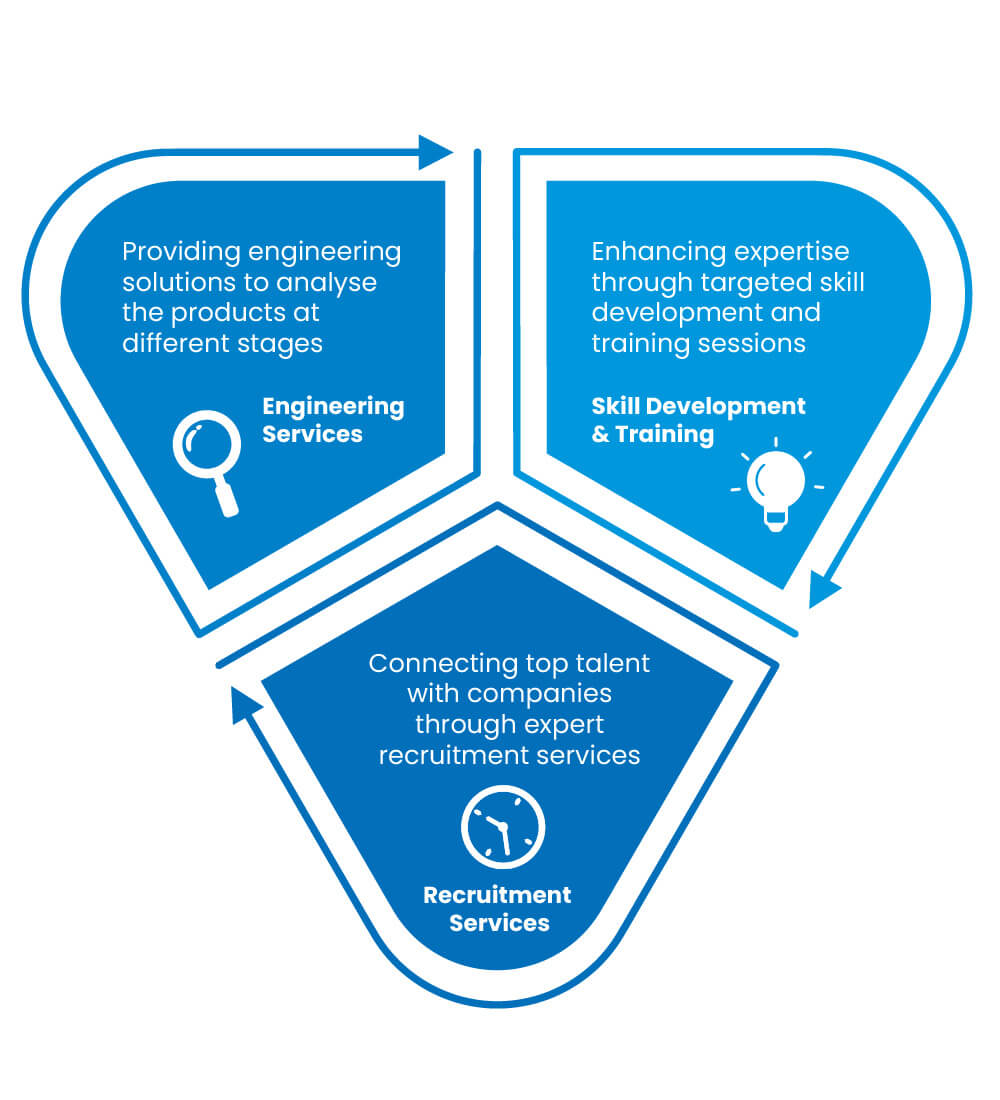
Product Development Cycle

Get in Touch
If you’ve got questions or ideas you would like to share, send a message. For anything more specific, please use one of the addresses listed below.
Pune, India
U15, Runwal Platinum, NDA Road, Bavdhan, Pune, Maharashtra – 411021.
Find Us on Map
Chennai, India
320/B, Thiruvallur high road, Chennai,
Tamil Nadu – 600124
Find Us on Map
Support
+91-82618 81518
+91-99433 04676
Our Email
info@varphi.in
Let's Talk About Your Project
After we get some information from you, we’ll set up a time to discuss your project in further detail.